Introduction:
Bone cancer, a rare but potentially serious form of cancer, can manifest through persistent bone ache. While occasional discomfort is a common part of life, understanding when to be concerned about bone pain and seeking timely medical attention is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intricacies of bone cancer, delve into the nuances of bone ache, and discuss the signs that should prompt individuals to seek professional medical evaluation.
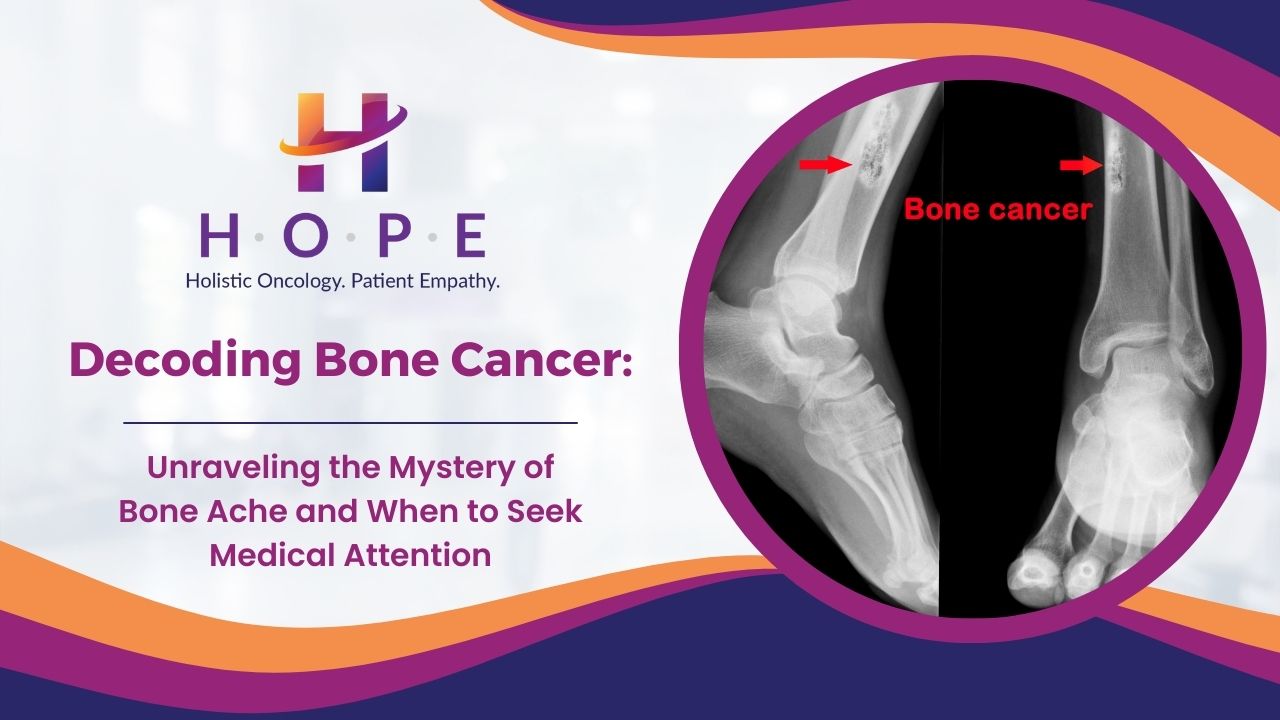
Understanding Bone Cancer:
Bone cancer, characterized by the abnormal growth of cells within the bones, can either originate in the bone itself (primary bone cancer) or spread to the bones from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic bone cancer). Primary bone cancer is relatively rare, with osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma being some of the primary types. Secondary bone cancer is more common and often stems from cancers such as breast, lung, or prostate cancer that have metastasized to the bones.
The Role of Bone Ache:
Bone ache, a common symptom of bone cancer, is often misconstrued as routine discomfort or aging-related joint pain. However, persistent and unexplained bone pain, especially when accompanied by other concerning signs, should not be ignored. Understanding the characteristics of bone ache associated with bone cancer is crucial for early diagnosis.
When Should I Be Worried?
Persistent Pain Unresponsive to Treatment:
One of the primary red flags for bone cancer is persistent pain that does not respond to conventional pain relief methods such as rest, over-the-counter pain medications, or physical therapy. Unlike the transient discomfort associated with injuries or strain, bone cancer-related pain tends to linger and may even intensify over time.
Night Pain or Rest Pain:
Bone cancer often manifests as pain that is more pronounced during periods of rest or at night. Individuals may find that the ache disrupts their sleep and is not alleviated by changes in position or rest. This distinct pattern of pain can be indicative of bone cancer and should be thoroughly investigated.
Localized Pain with Swelling or Lumps:
While localized pain alone might not immediately raise concerns, when coupled with noticeable swelling or the development of lumps near the affected area, it becomes a significant cause for worry. Bone cancer can alter the bone structure, leading to swelling and palpable masses that should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Changes in Range of Motion:
Bone cancer can affect the adjacent joints and tissues, resulting in limitations in the range of motion. If you experience persistent stiffness, decreased flexibility, or difficulty moving a joint without an apparent cause, it is essential to consult a doctor for a thorough examination.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue:
Systemic symptoms such as unexplained weight loss and fatigue can accompany bone cancer. The abnormal growth of cancer cells can affect the body’s metabolism, leading to unintended weight loss. Persistent fatigue, not attributable to other factors, should also be taken seriously and investigated further.
Fractures or Bone Weakness:
Bone cancer can weaken the affected bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. If you experience a fracture or break without a significant trauma or injury, it could be a sign of an underlying bone-related issue, and medical attention should be sought promptly.
Radiating Pain:
Pain that radiates from one part of the body to another can be indicative of bone cancer. For example, pain originating in the hip and radiating down the leg may signal bone cancer affecting the pelvic or femoral bones. Understanding the location and nature of the pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
When to Seek Professional Evaluation:
If you experience any combination of the aforementioned signs or have persistent bone ache that raises concerns, it is imperative to seek professional medical evaluation. A healthcare provider, typically a primary care physician or an orthopedic specialist, will conduct a thorough physical examination, evaluate your medical history, and may order imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to assess the bones and surrounding tissues.
The Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection of bone cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Once bone cancer reaches an advanced stage, it becomes more challenging to manage and may require more aggressive interventions, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Regular check-ups, open communication with healthcare providers, and a proactive approach to addressing persistent symptoms are essential in ensuring timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion:
Bone ache, when persistent and unexplained, should not be dismissed as routine discomfort. Understanding the potential association with bone cancer and recognizing the accompanying signs are crucial steps in ensuring early detection and prompt intervention. Being vigilant about changes in your body, seeking medical attention for concerning symptoms, and collaborating with healthcare professionals are vital aspects of maintaining overall health. Remember, your well-being is a priority, and addressing bone ache with the seriousness it deserves can make a significant difference in the management of bone cancer.